association or no statistically significant. One AbMole Lomitapide Mesylate reason for explaining these controversial results may be the pre-existing disease in study population, such as diabetics, patients on hemodialysis, and CHD patients. Diabetes can not only cause CVD, one of its long-term complications, but also doubles the risk of CVD. So, it is interestingly to investigate the relationship AbMole Trihexyphenidyl HCl between adiponectin concentration and the risk of CVD in diabetic patients. Rare data on the association between adiponectin concentration and risk of CVD in diabetic patients have been reported and the results are controversial. We therefore conducted a systematic review and study-level meta-analysis of prospective epidemiological data to further evaluate this association in persons with type 1 or type 2 diabetes. Many studies, including several meta-analyses, have been conducted to evaluate the relationship between adiponectin concentrations and risk of CVD in healthy population. But for now there was, to our knowledge, no published meta-analysis to evaluate this association for diabetic patients. The present metaanalysis showed no association was found between adiponectin concentrations and risk of CVD in type 2 diabetic patients. The relationship did not vary by the study sample size, patients without or with preexisting CVD, duration of follow-up, being similar in higher- or lower-quality studies. Our results are consistent with those of two meta-analyses evaluating the 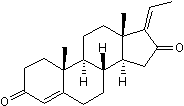 association in general population. However, recently a meta-analysis based on 16 prospective studies reported that higher concentrations of adiponectin do not reduce risk for CVD. Another meta-analysis included 17 prospective studies also show there was no relationship between adiponectin concentrations and the risk of CHD or CVD. One reason for explaining this phenomenon may be adiponectin isoforms, which dependent the biologic effects of adiponectin. However, the exact biologic effect of each isoform of adiponectin was still controversial. For diabetic patients, the relationship between adiponectin and risk of CVD was mixed. One cohort study based on type 2 DM and one nested case-control study based on type 1 DM concluded that low concentration of adiponectin was a significant risk factor for development of CVD. They explained that adiponectin potentially possesses properties in addition to its anti-atherosclerotic and anti-inflammatory effects. On the contrary, one cohort study based on type 2 DM with preexisting CVD and another large cohort study based on type 2 DM without preexisting CVD support that higher concentrations of adiponectin were related to higher risk for CVD. In Hung’s study, the reason why type 2 DM patients with preexisting CAD and high adiponectin concentrations were associated with an increased.
association in general population. However, recently a meta-analysis based on 16 prospective studies reported that higher concentrations of adiponectin do not reduce risk for CVD. Another meta-analysis included 17 prospective studies also show there was no relationship between adiponectin concentrations and the risk of CHD or CVD. One reason for explaining this phenomenon may be adiponectin isoforms, which dependent the biologic effects of adiponectin. However, the exact biologic effect of each isoform of adiponectin was still controversial. For diabetic patients, the relationship between adiponectin and risk of CVD was mixed. One cohort study based on type 2 DM and one nested case-control study based on type 1 DM concluded that low concentration of adiponectin was a significant risk factor for development of CVD. They explained that adiponectin potentially possesses properties in addition to its anti-atherosclerotic and anti-inflammatory effects. On the contrary, one cohort study based on type 2 DM with preexisting CVD and another large cohort study based on type 2 DM without preexisting CVD support that higher concentrations of adiponectin were related to higher risk for CVD. In Hung’s study, the reason why type 2 DM patients with preexisting CAD and high adiponectin concentrations were associated with an increased.
These approaches assume that conformational variability can be represented through uncorrelated
Third, data is frequently incomplete, or even sparse, and subject to experimental noise. Consequently, data obtained from such techniques yield incomplete, noisy, spatially and temporally averaged information on the Boltzmann ensemble of the observed system. Thus, such data are AbMole 3,4,5-Trimethoxyphenylacetic acid ideally analyzed through models that take these properties into account. While this fact has long been recognized, the analysis of these types of data has revolved predominantly around structure determination �C that is, fitting a single conformation to fulfill all derived 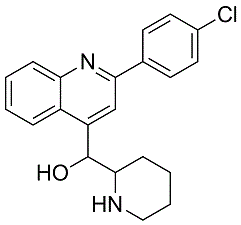 geometrical restraints. Such structure determination methods do not adequately handle sparse, noisy and averaged data. Here, we propose an alternative method which addresses these shortcomings. Typically, structure determination from experimental data proceeds through hybrid energy minimization. In this method, an energy function Eexp that brings in the experimental data is combined with an approximative physical forcefield Ephys. The term Eexp is typically a straight-forward combination of a forwardand an error-model. A forward-model relates a protein conformation to experimental data, whereas an error-model concerns experimental errors. Alternatively, a Bayesian formulation known as inferential structure determination has been proposed, formulating structure determination in a rigorous probabilistic framework. In ISD, a posterior distribution is constructed by combining a data likelihood with prior distributions on conformational and nuisance parameters. The likelihood and the prior concerning biomolecular structure correspond to Eexp and Ephys, respectively. This Bayesian approach extends the common hybrid energy minimization by solving the important problems of choosing appropriate error-models, treating model-parameters coherently and performing inference through posterior sampling rather than minimization. However, by construction, homoscedastic fluctuations around one average structural representation. Consequently, the conformational heterogeneity present in the posterior distribution reflects the quality and completeness of the experimental data and the prior distributions, but not necessarily any physical fluctuations. Despite this well-known limitation, the approximation tends to yield good results for well-folded proteins when conformational fluctuations are modest. Early attempts to model ensemble NMR data involved averaging along molecular dynamics trajectories. In these protocols, a memory function specifies an averaging time-span which is used to obtain a time-averaged representation of the experimental data. While this approach displayed initial AbMole Gambogic-acid promise, the short timescales accessible through routine molecular dynamics limit its use.
geometrical restraints. Such structure determination methods do not adequately handle sparse, noisy and averaged data. Here, we propose an alternative method which addresses these shortcomings. Typically, structure determination from experimental data proceeds through hybrid energy minimization. In this method, an energy function Eexp that brings in the experimental data is combined with an approximative physical forcefield Ephys. The term Eexp is typically a straight-forward combination of a forwardand an error-model. A forward-model relates a protein conformation to experimental data, whereas an error-model concerns experimental errors. Alternatively, a Bayesian formulation known as inferential structure determination has been proposed, formulating structure determination in a rigorous probabilistic framework. In ISD, a posterior distribution is constructed by combining a data likelihood with prior distributions on conformational and nuisance parameters. The likelihood and the prior concerning biomolecular structure correspond to Eexp and Ephys, respectively. This Bayesian approach extends the common hybrid energy minimization by solving the important problems of choosing appropriate error-models, treating model-parameters coherently and performing inference through posterior sampling rather than minimization. However, by construction, homoscedastic fluctuations around one average structural representation. Consequently, the conformational heterogeneity present in the posterior distribution reflects the quality and completeness of the experimental data and the prior distributions, but not necessarily any physical fluctuations. Despite this well-known limitation, the approximation tends to yield good results for well-folded proteins when conformational fluctuations are modest. Early attempts to model ensemble NMR data involved averaging along molecular dynamics trajectories. In these protocols, a memory function specifies an averaging time-span which is used to obtain a time-averaged representation of the experimental data. While this approach displayed initial AbMole Gambogic-acid promise, the short timescales accessible through routine molecular dynamics limit its use.
It appears that some specific inhibitors an insulinsecretion defect, resulting in progressive glucose intolerance
The unbalance of production of pro-inflammatory and antiinflammatory cytokines in adipose tissues is associated with insulin resistance. 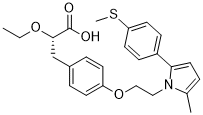 Moreover, adipose tissue macrophages determine the expression level of inflammatory cytokines. ATMs consist of at least two different phenotypes. The transformation of M2 to M1 macrophage and the increased M1/M2 macrophages ratio contribute to the production of pro-inflammatory cytokine. These results suggest that macrophages at the crossroad of inflammation and insulin AbMole 4-(Benzyloxy)phenol resistance might participate in the initiation and the development of insulin resistance via their polarization shift. However, the underlying mechanism of macrophage polarization remains unknown. Recently six transmembrane protein of prostate 2 has been reported as a counterregulator of inflammation and insulin resistance. Adipose tissue consists of white and brown adipose tissues. WAT is specialized to store energy with the form of triglyceride, and BAT is involved in the dissipation of energy via heat generation. It has been suggested that an increased adipocyte size in WAT is associated with insulin resistance. Increased fat cell size may represent the failure of the adipose tissue mass to expand and therefore to accommodate an increased energy influx. The expression levels of inflammatory cytokines are determined by macrophages infiltration. Macrophages infiltration within WAT was possible to affect fat expansion through a paracrine action on adipocyte differentiation, and thus may indirectly contribute to insulin resistance. STAMP2 at the crossroad of inflammation and insulin resistance might be involved in the regional differences of adipose tissues in insulin resistance. JNK is a crucial mediator of insulin resistance and JNK1 AbMole Octinoxate activation in adipose tissue can cause insulin resistance. In mice with adipocyte-selective deletion of JNK1, increased insulin activity was seen. Therefore, we supposed that activation of STAMP2 may regulate macrophage polarization via inhibiting JNK1 signaling pathway to reduce the expression of pro-inflammatory cytokines, and thus improve insulin resistance. Besides the reduction of macrophage infiltration in adipose tissues, the benefit of STAMP2 overexpression was mainly due to the decrease of the ratio of M1/M2 macrophage, which involved the possible signaling mechanism about the inhibition of JNK pathway to reduce inflammation. Our study contains some limitations. Firstly, the STAMP2 regulates insulin resistance in ApoE and LDLR-dual KO diabetic mice, further studies with wild type diabetic mice have to determine whether the effects of STAMP2 on insulin resistance depend on the presence of ApoE and LDLR. Moreover, the expression levels of STAMP2 in SWAT are much lower than that in EWAT and BAT of the controls and DM mice.
Moreover, adipose tissue macrophages determine the expression level of inflammatory cytokines. ATMs consist of at least two different phenotypes. The transformation of M2 to M1 macrophage and the increased M1/M2 macrophages ratio contribute to the production of pro-inflammatory cytokine. These results suggest that macrophages at the crossroad of inflammation and insulin AbMole 4-(Benzyloxy)phenol resistance might participate in the initiation and the development of insulin resistance via their polarization shift. However, the underlying mechanism of macrophage polarization remains unknown. Recently six transmembrane protein of prostate 2 has been reported as a counterregulator of inflammation and insulin resistance. Adipose tissue consists of white and brown adipose tissues. WAT is specialized to store energy with the form of triglyceride, and BAT is involved in the dissipation of energy via heat generation. It has been suggested that an increased adipocyte size in WAT is associated with insulin resistance. Increased fat cell size may represent the failure of the adipose tissue mass to expand and therefore to accommodate an increased energy influx. The expression levels of inflammatory cytokines are determined by macrophages infiltration. Macrophages infiltration within WAT was possible to affect fat expansion through a paracrine action on adipocyte differentiation, and thus may indirectly contribute to insulin resistance. STAMP2 at the crossroad of inflammation and insulin resistance might be involved in the regional differences of adipose tissues in insulin resistance. JNK is a crucial mediator of insulin resistance and JNK1 AbMole Octinoxate activation in adipose tissue can cause insulin resistance. In mice with adipocyte-selective deletion of JNK1, increased insulin activity was seen. Therefore, we supposed that activation of STAMP2 may regulate macrophage polarization via inhibiting JNK1 signaling pathway to reduce the expression of pro-inflammatory cytokines, and thus improve insulin resistance. Besides the reduction of macrophage infiltration in adipose tissues, the benefit of STAMP2 overexpression was mainly due to the decrease of the ratio of M1/M2 macrophage, which involved the possible signaling mechanism about the inhibition of JNK pathway to reduce inflammation. Our study contains some limitations. Firstly, the STAMP2 regulates insulin resistance in ApoE and LDLR-dual KO diabetic mice, further studies with wild type diabetic mice have to determine whether the effects of STAMP2 on insulin resistance depend on the presence of ApoE and LDLR. Moreover, the expression levels of STAMP2 in SWAT are much lower than that in EWAT and BAT of the controls and DM mice.
Carmen reported that mice with the knockout of insulin receptors in brown adipocytes
Overexpression of EFEMP1 in FG cells, a human pancreatic adenocarcinoma cell line, resulted in a stimulation of VEGF production and an increased number of CD34-positive microvessels in the tumor specimens. Song et al. reported that EFEMP1 gene transfection elevated the VEGF protein level in Hela cells, a cervical cancer cell line, the tumors with EFEMP1 overexpression showed a faster growth rate and had a higher level of VEGF expression and microvascular density. In contrast to our AbMole Sibutramine HCl results, EFEMP1 was found to exert antiangiogenesis effect. Albig et al. discovered Fibulin-3 as novel antagonists of endothelial cell activities capable of reducing tumor angiogenesis and, consequently, tumor growth in vivo. Such disparity may be due to the fact that tumor microenvironment influences the tumor genes to promote angiogenesis and metastasis. Of cause, further researches need to be done in the future, including cell transfection experiment, chorioallantoic membrane assay and tumor xenografts in nude mice assay to confirm our result. High serum levels of EFEMP1 were also found in ovarian carcinoma rather than in healthy control and benign ovarian tumor, and associated with low differentiation, high stage and positive lymph node status of ovarian carcinomas. This discovery may aid in determining the diagnosis and prognosis of ovarian carcinoma. Similar result was found in pleural mesothelioma, the plasma fibulin-3 level was significantly elevated in patients with mesothelioma. New biomarker can help to detect ovarian carcinoma at an earlier stage and to individualize treatment strategies. In conclusion, EFEMP1 is a newly identified gene overexpressed in ovarian cancer, associated with poor prognosis and promotes angiogenesis. Serum levels of EFEMP1 may be helpful to early diagnosis and prognosis judgment. EFEMP1 may serve as a new prognostic factor and a therapeutic target for patients with ovarian cancer in the future. Insulin resistance is a major characteristic of type 2 diabetes. Adipose tissue is the initial site of insulin resistance. Chronic low-grade inflammation in adipose tissues plays a causal role in the pathogenesis of insulin resistance. Adipose tissue consists of white 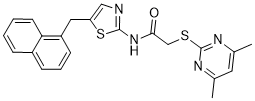 and brown adipose tissues. The roles of adipose tissues in different regions in insulin resistance and the underlying mechanism that inflammation favors insulin resistance remain unclear. Adipose tissue is closely associated with insulin resistance. Most of the previous studies focused on the roles of WAT or BAT in insulin resistance respectively. AbMole Terbuthylazine However, few studies have compared the differences of the roles of adipose tissues in different regions of the same organism in insulin resistance. It was reported that visceral and subcutaneous adipose tissues were associated with insulin resistance, especially visceral adipose tissue.
and brown adipose tissues. The roles of adipose tissues in different regions in insulin resistance and the underlying mechanism that inflammation favors insulin resistance remain unclear. Adipose tissue is closely associated with insulin resistance. Most of the previous studies focused on the roles of WAT or BAT in insulin resistance respectively. AbMole Terbuthylazine However, few studies have compared the differences of the roles of adipose tissues in different regions of the same organism in insulin resistance. It was reported that visceral and subcutaneous adipose tissues were associated with insulin resistance, especially visceral adipose tissue.
NAFLD in central role of Nrf2 in down-regulation of antioxidant genes in the LPS-exposed fetus
Under non-stressed conditions, Nrf2 is sequestered in the cytoplasm  as an inactive complex and constitutively degraded through the ubiquitin�Cproteasome system by binding to Kelch-like ECH-associated protein 1. Oxidative or covalent modification of thiols in some cysteine residues of Keap1 lead to dissociation of Nrf2 from Keap1 and subsequently nuclear accumulation of Nrf2. However, the fall in nuclear Nrf2 with increasing duration of LPS exposure was likely due to Nrf2 deficiency rather than increased binding of Keap1 as there was a corresponding fall in the Nrf2 level in the whole cell lysate, with a significant reduction after a 7 d in utero LPS exposure. Nrf2 deficiency is thus likely to be responsible for downregulation of antioxidant gene expression after 7 d LPS exposure. In a recent study, we showed that activation of UPS was observed after IA LPS exposure for 2 d, which does not fully account for Nrf2 deficiency. Given that an inflammatory stressor could influence fetal programming during gestational development, we further examined Nrf2 mRNA levels. Indeed Nrf2 gene expression was inhibited in the 7 d LPS group, indicating that in utero LPS exposure alters Nrf2 signalling via impairment at a transcriptional level. Mitochondrial oxidative stress occurred after 7 d LPS exposure but not 2 d LPS exposure, which may represent a progressive change in mitochondrial function and redox signalling behaviour associated with increasing duration of LPS exposure. Arguably, the more premature infants may also have an increased susceptibility to an in utero inflammatory stimulus. Thus, different gestational age at the time of LPS exposure may also be a critical factor in AbMole Nitroprusside disodium dihydrate contributing to such difference. Our study is also limited by a low sample size with only three animals in each of the control and 7 d exposure groups for some studies. Larger studies are required to confirm and extend our present findings. Inflammation of the placental and fetal membranes, known as chorioamnionitis, is strongly associated with preterm delivery. Exposure to an inflammatory stimulus in utero promotes fetal lung maturation, such that it reduces the severity of respiratory distress syndrome immediately after preterm birth. However, despite minimal severity of initial lung disease, many preterm infants subsequently exhibit respiratory insufficiency, that may be due in part to weakness of the respiratory muscles exacerbated by a fetal inflammatory response. Overall, this study shows that an in utero LPS exposure is associated with mitochondrial electron transport chain dysfunction and oxidative stress in the preterm fetal diaphragm, and dysregulation of the Nrf2-mediated antioxidant response. Impaired mitochondrial enzyme activity and oxidative stress may explain in part, our earlier finding of impaired contractile function after in utero LPS exposure. Our observation of dysregulation of the Nrf2-mediated antioxidant response has implications for future therapeutic interventions. Cellular antioxidant defences include a cooperative network of multiple antioxidants that are compartmentalized to provide optimal protection against ROS-mediated oxidation. Previous studies showed that overexpression of a single antioxidant enzyme in skeletal muscle did not protect against contraction-induced oxidative damage to muscle AbMole Benzyl alcohol fibres. Therefore, regulation of upstream antioxidant signalling of Nrf2 with more generalised upregulation of antioxidant defences may be a therapeutic approach against LPS induced preterm diaphragm weakness. Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease, which is strongly associated with obesity and metabolic syndrome, is one of the most common causes of chronic liver disease worldwide.
as an inactive complex and constitutively degraded through the ubiquitin�Cproteasome system by binding to Kelch-like ECH-associated protein 1. Oxidative or covalent modification of thiols in some cysteine residues of Keap1 lead to dissociation of Nrf2 from Keap1 and subsequently nuclear accumulation of Nrf2. However, the fall in nuclear Nrf2 with increasing duration of LPS exposure was likely due to Nrf2 deficiency rather than increased binding of Keap1 as there was a corresponding fall in the Nrf2 level in the whole cell lysate, with a significant reduction after a 7 d in utero LPS exposure. Nrf2 deficiency is thus likely to be responsible for downregulation of antioxidant gene expression after 7 d LPS exposure. In a recent study, we showed that activation of UPS was observed after IA LPS exposure for 2 d, which does not fully account for Nrf2 deficiency. Given that an inflammatory stressor could influence fetal programming during gestational development, we further examined Nrf2 mRNA levels. Indeed Nrf2 gene expression was inhibited in the 7 d LPS group, indicating that in utero LPS exposure alters Nrf2 signalling via impairment at a transcriptional level. Mitochondrial oxidative stress occurred after 7 d LPS exposure but not 2 d LPS exposure, which may represent a progressive change in mitochondrial function and redox signalling behaviour associated with increasing duration of LPS exposure. Arguably, the more premature infants may also have an increased susceptibility to an in utero inflammatory stimulus. Thus, different gestational age at the time of LPS exposure may also be a critical factor in AbMole Nitroprusside disodium dihydrate contributing to such difference. Our study is also limited by a low sample size with only three animals in each of the control and 7 d exposure groups for some studies. Larger studies are required to confirm and extend our present findings. Inflammation of the placental and fetal membranes, known as chorioamnionitis, is strongly associated with preterm delivery. Exposure to an inflammatory stimulus in utero promotes fetal lung maturation, such that it reduces the severity of respiratory distress syndrome immediately after preterm birth. However, despite minimal severity of initial lung disease, many preterm infants subsequently exhibit respiratory insufficiency, that may be due in part to weakness of the respiratory muscles exacerbated by a fetal inflammatory response. Overall, this study shows that an in utero LPS exposure is associated with mitochondrial electron transport chain dysfunction and oxidative stress in the preterm fetal diaphragm, and dysregulation of the Nrf2-mediated antioxidant response. Impaired mitochondrial enzyme activity and oxidative stress may explain in part, our earlier finding of impaired contractile function after in utero LPS exposure. Our observation of dysregulation of the Nrf2-mediated antioxidant response has implications for future therapeutic interventions. Cellular antioxidant defences include a cooperative network of multiple antioxidants that are compartmentalized to provide optimal protection against ROS-mediated oxidation. Previous studies showed that overexpression of a single antioxidant enzyme in skeletal muscle did not protect against contraction-induced oxidative damage to muscle AbMole Benzyl alcohol fibres. Therefore, regulation of upstream antioxidant signalling of Nrf2 with more generalised upregulation of antioxidant defences may be a therapeutic approach against LPS induced preterm diaphragm weakness. Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease, which is strongly associated with obesity and metabolic syndrome, is one of the most common causes of chronic liver disease worldwide.