Previous meta-analyses of studies investigated the prognostic value of molecular markers in different malignancies. These include VEGF and p53. To date, no such Saikosaponin-C meta-analysis evaluated ENT1 in pancreatic cancer treated with gemcitabine. Furthermore, low hENT1 has been associated with poor prognosis in pancreatic cancer managed with gemcitabine-based chemotherapy. Other studies have not shown any significant link between hENT1 and PCGC survival. However, the number of patients included in each study was small. Therefore, it was essential to combine and analyze the data to obtain acceptable results. In the present meta-analysis, we enrolled 12 studies related to the effects of low hENT1 expression on PCGC survival. In all these studies, hENT1 expression was detected by immunohistochemistry or PCR with surgical specimens. Meta-analysis suggested that low hENT1 was a factor associated with poor prognosis in PCGC. We further conducted subgroup analysis, in which hENT1 expression was measured by IHC. The results showed that low expression of hENT1 was closely associated with poor prognosis in patients with PCGC. Furthermore, hENT1 expression by PCR also showed significant impact on patients’ OS. The recent PRODIGE 4/Accord 11 trial results have expanded the therapeutic options in metastatic PAC, by demonstrating the superiority of FOLFIRINOX regimen in comparison with gemcitabine alone. This study included only patients who were aged below 76 years, with a good performance status, no cardiac ischemia, and normal or nearly normal bilirubin levels. However, no study investigated whether this regimen or other regimens were indicated for patients with low hENT1 expression in an adjuvant setting. Several studies reported methods involving histopathologic or cytopathologic diagnosis, including US- and CT-guided percutaneous biopsy, transpapillary pancreatic duct biopsy, and cytologic evaluation of pancreatic juice obtained via ERCP. The ability to visualize small lesions with EUS is excellent, and, unlike other methods, the entire pancreas is readily imaged. Thus, EUS-FNA is widely used as a cytological and histological sample collection tool in pancreatic cancer. Evaluation of hENT1 in pancreatic cancer tissue acquired with minimally invasive procedures warrants further study to determine the potential to individualize gemcitabine therapy in the majority of pancreatic cancer patients who present with locally advanced or metastatic disease. Meta-analysis of prognostic literature is associated with a number of inherent limitations. Retrospective study design is one of the key limitations. Only three of the studies included in the current meta-analysis involve a prospective design. The availability and adequacy of corresponding clinicopathological data is also a significant consideration in retrospective studies of this type. We identified several studies reporting incomplete histopathological datasets. Other disadvantages include the following: First, we failed to review unpublished articles and abstracts, as most of the data were not required. Second, we included 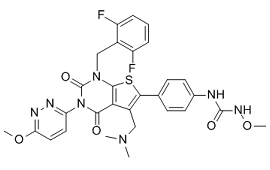 eligible English and Chinese studies only, suggesting a Gentiopicrin language bias. Third, HR calculation from data or extrapolation from survival curves in the articles, in the absence of directly reported HR values, introduced an element of decreased reliability. Our meta-analysis also displayed significant strengths. First, the quality of studies included in the meta-analysis was satisfactory and strictly met the inclusion criteria. Second, the summary risk estimates of our study did not show any evidence of heterogeneity and publication bias. Third, we performed subgroup analysis by measuring hENT1.
eligible English and Chinese studies only, suggesting a Gentiopicrin language bias. Third, HR calculation from data or extrapolation from survival curves in the articles, in the absence of directly reported HR values, introduced an element of decreased reliability. Our meta-analysis also displayed significant strengths. First, the quality of studies included in the meta-analysis was satisfactory and strictly met the inclusion criteria. Second, the summary risk estimates of our study did not show any evidence of heterogeneity and publication bias. Third, we performed subgroup analysis by measuring hENT1.
These dynamic changes are relatively Sfrp5 levels with pro-inflammatory cytokines
Clinical samples are clearly required to substantiate the notion that metabolic and/or inflammatory disturbances impact on the mode of Sfrp5 action. The present study further showed that Sfrp5 inhibits insulin action in primary human adipocytes under basal culture conditions. In support of a role for Sfrp5 in impairing insulin action are data from a clinical study on obese subjects without diabetes in which circulating Sfrp5 levels were found to be associated with HOMA-IR, and a study on Chinese subjects which reported increased circulating Sfrp5 levels in patients with T2D compared to subjects without diabetes. In contrast, two other studies on Asians showed decreased circulating Sfrp5 levels in patients with T2D versus subjects with normal glucose tolerance, and reported a negative association between plasma levels of Sfrp5 and HOMA-IR and. Also in mice conflicting data have been reported. One study showed that loss of functional Sfrp5 mitigated increases in serum leptin levels, as well as the induction of glucose intolerance and insulin resistance after highfat feeding. In contrast, Sfrp5 deficiency led to AbMole Capromorelin tartrate severe glucose intolerance and further impaired insulin-stimulated phosphorylation of Akt in adipose tissue following high-fat feeding as compared to wild-type mice. This was associated with increased activation of the JNK signaling pathway, which inhibits insulin action via phosphorylation of Ser307 of insulin receptor substrate 1. In line with observations in 3T3-L1 adipocytes, we observed that Sfrp5 had no effect on JNK phosphorylation in primary human adipocytes, neither under basal conditions nor following exposure to TNFa. Therefore, it seems unlikely to ascribe the inhibition of insulin signaling induced by Sfrp5 in human adipocytes to Ser307-phosphorylation of insulin receptor substrate 1. Nevertheless, a limitation of the present study is that we did not examine additional pathways potentially involved in the induction of insulin resistance by Sfrp5, such as activation of the proteasome or the mammalian target of rapamycin complex 1 signaling cascade. The value of such investigations would, AbMole Folic acid however, benefit from recognition of the confounding factors that could explain the conflicting data observed in the in vivo studies. Another aspect that should be considered in this context is that we failed to observe any effect of Sfrp5 on hSkMC. Consequently, the 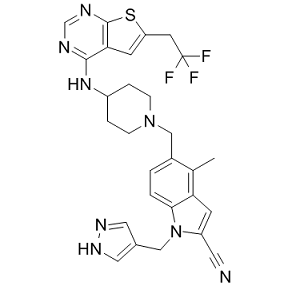 action of Sfrp5 may be tissue-specific. Sfrp5 is known to act as an antagonist for Wnt5a, which in turn activates Wnt signaling through binding to the frizzled receptors. Although Wnt5a is expressed in hSkMC, one may hypothesize that hSkMC do not release Wnt5a, and are therefore unresponsive to Sfrp5. However, we found that even in the presence of recombinant Wnt5a, hSkMC remained unresponsive to Sfrp5 with regard to the parameters examined in this study. This suggests that Wnt5a might not be the only target molecule for Sfrp5 and that there might be other molecules and/or receptors for Sfrp5 associated with its mechanisms of action. For example, Sfrp5 has also been described to antagonize the action of Wnt3a in mouse adipose tissue and of Wnt11 during organogenesis in Xenopus and zebrafish development. However, since Sfrp5 mainly targets the non-canonical Wnt pathway, detailed studies towards the effects of Sfrp5 and/or its Wnt target molecules in hSkMC are currently hampered by a lack of knowledge on the identity of the molecules affected by this non-canonical signaling cascade. Enzymes exhibit both fast changes and long-lived differences in activity. Fast changes give rise to what is called “dynamic heterogeneity” in which relatively low energy barriers ) enable rapid interconversion between different conformations at ambient temperature.
action of Sfrp5 may be tissue-specific. Sfrp5 is known to act as an antagonist for Wnt5a, which in turn activates Wnt signaling through binding to the frizzled receptors. Although Wnt5a is expressed in hSkMC, one may hypothesize that hSkMC do not release Wnt5a, and are therefore unresponsive to Sfrp5. However, we found that even in the presence of recombinant Wnt5a, hSkMC remained unresponsive to Sfrp5 with regard to the parameters examined in this study. This suggests that Wnt5a might not be the only target molecule for Sfrp5 and that there might be other molecules and/or receptors for Sfrp5 associated with its mechanisms of action. For example, Sfrp5 has also been described to antagonize the action of Wnt3a in mouse adipose tissue and of Wnt11 during organogenesis in Xenopus and zebrafish development. However, since Sfrp5 mainly targets the non-canonical Wnt pathway, detailed studies towards the effects of Sfrp5 and/or its Wnt target molecules in hSkMC are currently hampered by a lack of knowledge on the identity of the molecules affected by this non-canonical signaling cascade. Enzymes exhibit both fast changes and long-lived differences in activity. Fast changes give rise to what is called “dynamic heterogeneity” in which relatively low energy barriers ) enable rapid interconversion between different conformations at ambient temperature.
Infected with influenza had significantly higher hospitalization rates than cases infected
With Influenza A pdm09. In our study, Influenza B followed pdmH1N1 as a close second in both ILI and SARI cases when compared to other influenza A subtypes. Therefore, the effect of yearround presence of influenza B AbMole BI-9564 viruses on the health care system must be estimated alongside analysis of the influenza A associated morbidity and mortality. The fact that a novel pandemic virus was co-circulating in the predicted influenza season offered an opportunity for comparison of epidemiology, clinical presentation and outcome for seasonal versus pandemic viruses. We know pandemic viruses characteristically infect younger age groups and healthy adults in comparison to seasonal influenza where extremes of age and individuals with co-morbid conditions are the susceptible population groups. In contrast, pandemic viruses such as A pdm09 target young adult population from 21-40 years in age. Our study showed detection of A/ H1N1 and A/H3N2 was higher in children less than 10 years of age than A/pdm09 and Influenza B which reflects the observations of Bin Cao et. al., who demonstrated higher susceptibility rates for A/H3N2 and A/H1N1 in children below 10 years of age. There is limited available data that shows that other respiratory viruses such as respiratory syncytial virus, human metapneumovirus and adenoviruses cocirculate in influenza season causing ILI and SARI infections and could partly explain lower positivity rates in children for pandemic H1N1. Inflammation is a complex physiological process involving numerous receptor-ligand interactions between leukocytes and the endothelial lining of the blood vessel that ultimately lead to the trafficking of leukocyte subsets throughout the body. Numerous diseases are associated with dysregulated inflammation, including rheumatoid arthritis, asthma, psoriasis, thrombotic disorders, cancer, and autoimmune disease. Bromelain is a mixture of several cysteine proteases isolated from pineapple extracts, and is taken as a complementary antiinflammatory treatment. Bromelain is known to alter multiple cell surface molecules involved in the adhesion and activation of leukocytes leading to anti-inflammatory, fibrinolytic, and antithrombotic effects in vivo and in vitro. Previous reports have investigated the effects of bromelain treatment on neutrophil migration in response to AbMole Nitroprusside disodium dihydrate chemokines. However, bromelain’s ability to alter cell surface molecules involved in the initial tethering and rolling of leukocytes on the inflamed endothelium has not been investigated to date. Among the enzymes present in bromelain extract is stem bromelain, which was used in this study and will be simply referred to as bromelain herein. Endothelial-expressed P-selectin and E-selectin play central roles during the initiation of 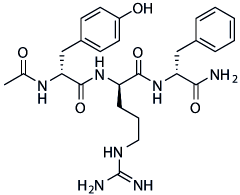 an inflammatory response.
an inflammatory response.
IL-8 plays an important role in promoting the formation of atherosclerosis
In conclusion, we present the theoretical foundations of a Bayesian principle to infer ensembles of protein structures from noisy experimental data subject to ensemble and time averaging. We demonstrate the principle constitutes a generalization of ISD and previously proposed maximum entropy restraining approaches. Finally, the principle is successfully evaluated using synthetic experimental data of a small idealized system. Cerebrovascular diseases have become the most AbMole Corosolic-acid common cause of death in China. Atherosclerotic cerebral infarction is the most common form of stroke. Many studies have indicated that inflammation plays an important role in the formation of atherosclerosis and ischemic brain injury. Interleukin-8 is a typical member of the CXC chemokine subfamily and a strong chemoattractant factor for neutrophils, basophilic leukocytes 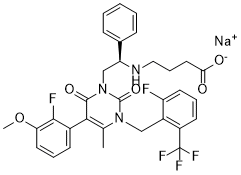 and T lymphocytes via firm binding to its receptors, CXCR1 or CXCR2. As a strong mediator of inflammation, involved in the process of brain injury after acute cerebral infarction. Many studies have indicated that genetic polymorphisms were associated with the occurrence of cerebral infarction. The IL-8 mRNA levels expressed in peripheral blood mononuclear cells has been shown to increase rapidly during the acute stage of cerebral infarction. The IL-8 concentrations also increased rapidly in the plasma and CSF of patients with acute ischemic stroke. Currently, there have been few association studies between the SNPs of IL-8 and cerebral infarction. No previous study has investigated the association of the +781C/T polymorphism with atherosclerotic cerebral infarction, especially in the Han Chinese population. Our study revealed that the +781C/T polymorphism in IL-8 was not associated with atherosclerotic cerebral infarction. Taken together, this result and the findings of other studies might demonstrate that the common SNPs of IL-8 have no associations with cerebral infarction. Atherosclerotic cerebral infarction is a disease caused by a combination of multiple factors and genes, and thus the effects produced by one or several SNPs on the occurrence of diseases are very slight and the risk of an individual suffering from cerebral infarction may be determined by the synergy of some risk factors. Whether the +781C/T polymorphism of IL-8 affects the occurrence and development of cerebral infarction by interacting with other genes requires further research. The OCSP classification of cerebral infarction revealed that brain areas were AbMole Ellipticine damaged by the obstruction of certain corresponding feeding arteries after ischemic stroke. IL-8 is involved in the process of brain injury after atherosclerotic cerebral infarction, but the contributions of the +781C/T genotype and allele frequencies to the OCSP subtypes were not significantly different in this study.
and T lymphocytes via firm binding to its receptors, CXCR1 or CXCR2. As a strong mediator of inflammation, involved in the process of brain injury after acute cerebral infarction. Many studies have indicated that genetic polymorphisms were associated with the occurrence of cerebral infarction. The IL-8 mRNA levels expressed in peripheral blood mononuclear cells has been shown to increase rapidly during the acute stage of cerebral infarction. The IL-8 concentrations also increased rapidly in the plasma and CSF of patients with acute ischemic stroke. Currently, there have been few association studies between the SNPs of IL-8 and cerebral infarction. No previous study has investigated the association of the +781C/T polymorphism with atherosclerotic cerebral infarction, especially in the Han Chinese population. Our study revealed that the +781C/T polymorphism in IL-8 was not associated with atherosclerotic cerebral infarction. Taken together, this result and the findings of other studies might demonstrate that the common SNPs of IL-8 have no associations with cerebral infarction. Atherosclerotic cerebral infarction is a disease caused by a combination of multiple factors and genes, and thus the effects produced by one or several SNPs on the occurrence of diseases are very slight and the risk of an individual suffering from cerebral infarction may be determined by the synergy of some risk factors. Whether the +781C/T polymorphism of IL-8 affects the occurrence and development of cerebral infarction by interacting with other genes requires further research. The OCSP classification of cerebral infarction revealed that brain areas were AbMole Ellipticine damaged by the obstruction of certain corresponding feeding arteries after ischemic stroke. IL-8 is involved in the process of brain injury after atherosclerotic cerebral infarction, but the contributions of the +781C/T genotype and allele frequencies to the OCSP subtypes were not significantly different in this study.
Architecturally it remains only an approximation of naturally occurring human SCC
Firstly, the subcutaneous space is an artificial microenvironment where cutaneous SCC does not develop spontaneously. This is a common choice for animal models nevertheless, because of its accessibility and convenience. Secondly, though our explants retain their epithelial basement membrane zone, it theoretically has a less important role once transplanted to the subcutaneous space. This is an issue insofar as basement membrane integrity contributes to malignancy, which is the case in a wide range of epithelial cancers such as breast, prostate, lung, kidney, and skin. Since in this case we select tumors based on invasive histology, however, the basement membrane is compromised from the start and we need not rely on its integrity to modulate malignancy. We noted volume contraction after 28 days however human SCC cells continued to proliferate and apoptosis remained at pre implantation levels. Volume contraction may have been to an initial lag in engraftment. We will address this and other issues as we develop the model further and extend the time course. Another limitation to this model is the absence of metastasis. This preliminary study was only four weeks, which is a short timeframe to show metastasis. It is likely necessary to extend the time course to fully realize the potential of the model. It may be challenging to achieve metastasis with implantation based models.Due to the limitations mentioned above, more population-based well-designed cohort studies will be needed to confirm our results. The updating of this meta-analysis will give us more information and may help inform clinical practice guidelines in the future. The eukaryotic protozoan parasite Entamoeba histolytica is the causative agent of amoebiasis, a global health threat responsible for an estimated million cases of invasive colitis or liver abscess and up to 100,000 deaths per year. Although the parasite has a worldwide distribution, it predominantly affects individuals of lower socioeconomic status, who live in developing countries. Protein phosphorylation is a key post-translational modification that is regulated by the competing activities of protein kinases and protein phosphatases. The net phosphorylation state relies on a delicate balance between PKs, which catalyse phosphate addition, and PPs, catalysing phosphate removal. Thus it is not surprising that disease conditions often correlate with alteration of the cell phosphorylation profile as a consequence of a perturbation of kinase and/or phosphatase activities. PKs are currently the pharmaceutical industry’s second largest drug targets, which are extensively studied.