The univariate analysis revealed a hospital mortality rate of 36.8%, with an odds ratio of 43.8. De Santo et al.evaluated 1,424 Clofentezine patients undergoing cardiac valve surgery and observed a 43.8% hospital mortality rate in patients classified as RIFLE�CFailure, with an odds ratio of 30. Even minimal changes in postoperative SCr were associated with a significant reduction in short and long-term survival. The SCr elevation might be associated with increased morbidity and mortality, even when the change did not exceed normal values. After cardiac surgery, AKI might occur in up to 48% of patientsand up to 9.6% of patients require RRT, particularly those with preoperative renal dysfunction. In our sample, 2% of patientsrequired RRT, in the first 7 postoperative 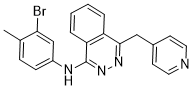 days. Epidemiological studies have reported an RRT requirement of approximately 2.6% to 4.9%. Our lower incidence of RRT was associated with the fact that the need for dialysis treatment was evaluated only in the first seven days after surgery but the similarity of other studies suggests that although each center has different patient populations and criteria for indicating RRT, the average incidence of severe AKI requiring RRT is approximately 4%. In our study, the mortality of KDIGO stage 3 patients needing RRT peaked at 62%, in contrast with the mortality of patients without postoperative AKI. Although the mortality of patients treated with RRT after cardiac surgery declined, in most studies, this factor remained greater than 40%. We also found that age, female gender and CPB times are predictors of 30-day mortality after cardiac surgery. Age and female gender are traditional predictors of early and late mortality after cardiac surgery and are present in most contemporary operative risk scores. Many studies have found Pancuronium dibromide higher mortality rates after cardiac surgery in female genderbut not all. The higher mortality could be explained by differences in baseline characteristics such as older age, higher body mass index, more cardiovascular risk factors and comorbidities. Considering these possible confounders, we found that female gender was an independent risk factor for 30-day mortality after cardiac surgery. Cardiopulmonary bypass times were also implied to increase mortality after cardiac surgery. CPB is associated with significant hemodynamic changes, and the maintenance of cardiovascular stability during CPB requires the interplay between the function of the CPB machine and patient factors. Thus, any decrease in renal perfusion during CPB, depending on its magnitude and duration, can lead to significant cellular injury. Currently, only three studies have used the KDIGO classification to evaluate patients after cardiac surgery. In the first study, Ho et al.evaluated the change in SCrduring the first 6 hours after surgery in 350 patients undergoing CABG or CVS. The results showed that 14% of patients developed AKI according to the KDIGO criteria, with greater than 10% variation in SCr immediately after surgery, strongly associated with subsequent AKI after cardiac surgery. In the second study, Sampaio et al.evaluated the incidence and risk factors for AKI in 321 patients after cardiac surgery according to RIFLE, AKIN and KDIGO criteria. The incidence of AKI ranged from 15�C51%, and the adjusted Cox regression analysis revealed that only cases diagnosed, the requirement for RRT and prolonged hospitalization.
days. Epidemiological studies have reported an RRT requirement of approximately 2.6% to 4.9%. Our lower incidence of RRT was associated with the fact that the need for dialysis treatment was evaluated only in the first seven days after surgery but the similarity of other studies suggests that although each center has different patient populations and criteria for indicating RRT, the average incidence of severe AKI requiring RRT is approximately 4%. In our study, the mortality of KDIGO stage 3 patients needing RRT peaked at 62%, in contrast with the mortality of patients without postoperative AKI. Although the mortality of patients treated with RRT after cardiac surgery declined, in most studies, this factor remained greater than 40%. We also found that age, female gender and CPB times are predictors of 30-day mortality after cardiac surgery. Age and female gender are traditional predictors of early and late mortality after cardiac surgery and are present in most contemporary operative risk scores. Many studies have found Pancuronium dibromide higher mortality rates after cardiac surgery in female genderbut not all. The higher mortality could be explained by differences in baseline characteristics such as older age, higher body mass index, more cardiovascular risk factors and comorbidities. Considering these possible confounders, we found that female gender was an independent risk factor for 30-day mortality after cardiac surgery. Cardiopulmonary bypass times were also implied to increase mortality after cardiac surgery. CPB is associated with significant hemodynamic changes, and the maintenance of cardiovascular stability during CPB requires the interplay between the function of the CPB machine and patient factors. Thus, any decrease in renal perfusion during CPB, depending on its magnitude and duration, can lead to significant cellular injury. Currently, only three studies have used the KDIGO classification to evaluate patients after cardiac surgery. In the first study, Ho et al.evaluated the change in SCrduring the first 6 hours after surgery in 350 patients undergoing CABG or CVS. The results showed that 14% of patients developed AKI according to the KDIGO criteria, with greater than 10% variation in SCr immediately after surgery, strongly associated with subsequent AKI after cardiac surgery. In the second study, Sampaio et al.evaluated the incidence and risk factors for AKI in 321 patients after cardiac surgery according to RIFLE, AKIN and KDIGO criteria. The incidence of AKI ranged from 15�C51%, and the adjusted Cox regression analysis revealed that only cases diagnosed, the requirement for RRT and prolonged hospitalization.
Monthly Archives: April 2019
These differences identification and validation of suitable reference genes for miRNA qPCR assay
Despite the surge of interest in miRNA identification and quantification during the epileptogenic Acetylcorynoline process. Ideally, reference genes should present high expression stability levels in different experimental conditions. The evaluation of a panel of five candidate reference genes to Dimesna determine the most reliable one for accurate normalization of gene expression in the systemic PILO-model indicated twoas the most stable in the hippocampus of rats from all experimental and control groups. Depending on the software used, the rank of these genes on a stability scale was slightly different, probably because of the different mathematical algorithm employed. We also considered whether selecting multiple reference genes in combination is better than selecting a single reference gene alone. The optimal number of reference genes which should be used for accurate normalization was determined by calculating the normalization factor. The use of more than the two most stable reference genes identifiedis not required as suggested by the V-value. In order to evaluate the functional significance of the results obtained for reference genes, we conducted a relative expression analysis of the miR-146a gene, whose pattern is already described for the PILO-injected model. miR-146a can be induced by different pro-inflammatory stimuli and has been shown to be upregulated in experimental models of epilepsy, as well as in human TLE. Indeed, in PILO and electrical stimulation TLE models, prominent upregulation of miRNA-146a was evident at 13 week after SE and persisted in the chronic phase. In human TLE with hippocampal sclerosis, increased astroglial expression of miR-146a was observed mainly in regions where neuronal cell loss and reactive gliosis occurred. Similarly, Iyer et al.showed an overexpression of mir-146a in epilepsyassociated glioneuronal lesions. It remains unclear how the induction of mir146 expression may contribute to the etiopathogenesis of TLE. Thus, Iyer et al.observed that seizures alone may not account for changes in miR-146a expression. Moreover, emerging data suggest that miR-146a is induced as a negativefeedback regulator of the glial-mediated inflammatory response associated to the epileptogenic process. This is 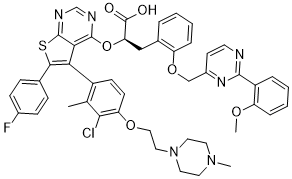 in line with other studies supporting an immunomodulatory role ascribed to miR-146a in several human neurodegenerative diseases associated with a strong inflammatory component. In fact, upregulation of miR146a has been detected in active multiple sclerosis lesions, in human Alzheimer diseasebrainand in prion disease, indicating an underlying common inflammatory response to different neurological insults. Accordingly, when normalized using the best combination of two or three reference genes, we observed that miR-146a transcript levels were significantly increased in the chronic stage. Interestingly, under our experimental conditions, the use of a reference gene individually for normalization leads to the relative transcript levels of the mir-146a gene to be different from those obtained with the best combinations of genes, and hence probably less accurate. This suggests, therefore, that an appropriate normalization strategy for miRNA expression during epileptogenesis requires the use of two or more reference genes. Curiously, in previous studies, under the same experimental conditions, in order to normalize protein-coding RNA expression, the use of just one of the stable reference genes produced a reliable measurement.
in line with other studies supporting an immunomodulatory role ascribed to miR-146a in several human neurodegenerative diseases associated with a strong inflammatory component. In fact, upregulation of miR146a has been detected in active multiple sclerosis lesions, in human Alzheimer diseasebrainand in prion disease, indicating an underlying common inflammatory response to different neurological insults. Accordingly, when normalized using the best combination of two or three reference genes, we observed that miR-146a transcript levels were significantly increased in the chronic stage. Interestingly, under our experimental conditions, the use of a reference gene individually for normalization leads to the relative transcript levels of the mir-146a gene to be different from those obtained with the best combinations of genes, and hence probably less accurate. This suggests, therefore, that an appropriate normalization strategy for miRNA expression during epileptogenesis requires the use of two or more reference genes. Curiously, in previous studies, under the same experimental conditions, in order to normalize protein-coding RNA expression, the use of just one of the stable reference genes produced a reliable measurement.
There is insufficient evidence to support the use of specific interventions to improve IVF treatment
A variety of regimens have been employed, including the use of increased gonadotropin doses, low dose gonadotropin-releasing hormoneagonists or antagonists, flare regimes, adjunctive growth hormone, minimal ovarian stimulation with clomiphene citrate, and natural cycle IVF. However, the ideal stimulation regimen for poor responders is currently unknown. The Cochrane review of poor responder interventions concluded that no Povidone iodine particular treatment offered clear benefit, or could be recommended. The management of poor responders therefore remains a significant challenge in assisted reproduction. In the last few years, a number of studies have suggested that dehydroepiandrosteronetreatment may be effective in poor responders. DHEA is now widely used in poor responders; recently, a world-wide survey showed that 26% of IVF clinicians in 45 countries add DHEA as an adjuvant to IVF treatment protocols in women with poor ovarian response. However, clinical evidence for DHEA on improvement of ovarian response and IVF outcome is still limited, the validity of the results of the earlier studies, especially the varied inclusion criteria, is a subject of debate. Recently, the Consensus Group for the European Society for Human Reproduction and Embryologydeveloped a new definition, the Bologna criteria, to help assigning more uniform patient groups in future clinical trials. However, no 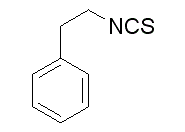 studies have been performed study to evaluate the potential effects of DHEA supplementation according to these standards. This study is the first to examine the effect of DHEA in poor ovarian responder patients that fulfill the Bologna criteria. According to our results, although the oocyte and embryo numbers were similar between the two groups, DHEA administration was associated with significantly higher implantation and ongoing PRs. DHEA is a mild androgen, produced as an intermediate step by the adrenal glandsand ovariesduring steroidogenesis. The circulating levels of DHEA decline markedly with advancing age. It is a very important prehormone for sex steroidogenesis. In the ovarian follicle, DHEA is converted to androstenedione and estrone, the source of testosterone and estradiol according to the two-cell theory. Casson first speculated that exogenous administration of DHEA could restore ovarian follicular sex steroidogenesis in elderly women. Since then, a few controlled studies with small Coptisine-chloride sample sizes have reported the benefits of DHEA administration in improving ovarian response and IVF outcome. However, since women with significant diminished ovarian reserve usually are reluctant to enter prospectively randomized studies that may assign them to placebo, because of the limited time remaining to conceive with use of their own oocytes, nearly all DHEA data represented lower levels of evidence. The first RCT study with small sample size regarding DHEA administration before IVF in poor responders was conducted by Wiser and associates, who showed a significantly higher cumulative live birth rate among the DHEA group. In contrast, another recent RCT study with larger sample size failed to show that DHEA supplementation enhances IVF-ICSI outcome in women with poor ovarian reserve. The meta-analysis which evaluated the effect of adjuvant androgensor androgen-modulating agentsin previous poor responders has failed to demonstrate any significant difference in the ongoing PRs.
studies have been performed study to evaluate the potential effects of DHEA supplementation according to these standards. This study is the first to examine the effect of DHEA in poor ovarian responder patients that fulfill the Bologna criteria. According to our results, although the oocyte and embryo numbers were similar between the two groups, DHEA administration was associated with significantly higher implantation and ongoing PRs. DHEA is a mild androgen, produced as an intermediate step by the adrenal glandsand ovariesduring steroidogenesis. The circulating levels of DHEA decline markedly with advancing age. It is a very important prehormone for sex steroidogenesis. In the ovarian follicle, DHEA is converted to androstenedione and estrone, the source of testosterone and estradiol according to the two-cell theory. Casson first speculated that exogenous administration of DHEA could restore ovarian follicular sex steroidogenesis in elderly women. Since then, a few controlled studies with small Coptisine-chloride sample sizes have reported the benefits of DHEA administration in improving ovarian response and IVF outcome. However, since women with significant diminished ovarian reserve usually are reluctant to enter prospectively randomized studies that may assign them to placebo, because of the limited time remaining to conceive with use of their own oocytes, nearly all DHEA data represented lower levels of evidence. The first RCT study with small sample size regarding DHEA administration before IVF in poor responders was conducted by Wiser and associates, who showed a significantly higher cumulative live birth rate among the DHEA group. In contrast, another recent RCT study with larger sample size failed to show that DHEA supplementation enhances IVF-ICSI outcome in women with poor ovarian reserve. The meta-analysis which evaluated the effect of adjuvant androgensor androgen-modulating agentsin previous poor responders has failed to demonstrate any significant difference in the ongoing PRs.
This rekindled my interest in the above compounds and I set out to understand the reaction further by elucidating its mechanism
One study has shown a correlation between the SNP of SLCO3A1 and QT prolongation in schizophrenic patients treated with iloperidone. Schizophrenia is known to be associated with a high prevalence of smoking. Meta-analyses of GWAS have also shown that SLCO3A1 is associated with nicotine dependence. As shown in a previous study, nicotine increases oxidative stress, activates NF-kB, and induces apoptosis. In our study, we have provided evidence that nicotine induction leads to enhanced NF-kB activation in the presence of SLCO3A1. These findings are consistent with the hypothesis that smoking exacerbates the course of CD due to allelic change of SLCO3A1. We are aware of limitations associated with this study due to the small sample size. As emphasized in the introduction, CD is still a low incidence/prevalence disease in Taiwan. Therefore, despite our best efforts to enroll patients, the sample size was small. We would like to see further validation of these results from other countries in the future. Secondly, the tissues used for control were not ideal. Theoretically, age-and sex-matched healthy individuals and subjects with non-IBD inflammationwould be more appropriate for the control group. However, in clinical practice, these conditions are not appropriate or indicated for endoscopy or surgery. Therefore, we were not able to obtain this Ergosterol tissue for use as control. Instead, we used colorectal cancer and intestine transplantation tissue since these are Gomisin-D obtainable in clinical practice. The gender ratio of colorectal cancer is similar to that of IBD in Taiwan. With respect to age, we performed a correlation 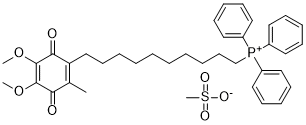 analysis of the expression of SLCO3A1 and age, and found no correlation between them. Therefore, we concluded that it would be acceptable to use the current control for interpreting the results. In conclusion, SLCO3A1 is a novel CD-associated gene based on our Illumina platform analysis and functional study results. Expression of SLCO3A1 activates the NF-kB transcription factor mediating inflammatory processes, consequently inducing increased activation of ERK and JNK phosphorylation and leading to a more intense and protracted NF-kB activation in intestinal epithelial cells. Active disease CD tissue expressed higher levels of SLCO3A1 compared with tissue analyzed from patients in remission. Stronger inflammation is associated with a greater chance of a perforated CD phenotype. Nicotine enhances the NFkB activation in the presence of SLCO3A1, which can partially explain smoking’s influence as an aggravating factor for CD. The atmospheric oxidation of group 13 metal alkyls is usually very rapid and uncontrollable, often resulting in combustion.However, controlled oxidation by limited exposure to oxygen gas results in the production of organoperoxide compounds, or alkoxide compounds through the decomposition of the former.It has been well established that the formation of the alkoxide occurs through an intermolecular oxygen transfer, not an intramolecular one.Thus, it is possible to isolate stable complexes bearing a strongly reducing metal-alkyl bond in close proximity of a strongly oxidizing metal-peroxide bond.However, it was demonstrated that spatial requirement plays an important part in the oxidation of group 13 metal alkyls. Recently I became interested in pursuing complexes that bear resemblance to methylalumoxane, a common co-catalyst.
analysis of the expression of SLCO3A1 and age, and found no correlation between them. Therefore, we concluded that it would be acceptable to use the current control for interpreting the results. In conclusion, SLCO3A1 is a novel CD-associated gene based on our Illumina platform analysis and functional study results. Expression of SLCO3A1 activates the NF-kB transcription factor mediating inflammatory processes, consequently inducing increased activation of ERK and JNK phosphorylation and leading to a more intense and protracted NF-kB activation in intestinal epithelial cells. Active disease CD tissue expressed higher levels of SLCO3A1 compared with tissue analyzed from patients in remission. Stronger inflammation is associated with a greater chance of a perforated CD phenotype. Nicotine enhances the NFkB activation in the presence of SLCO3A1, which can partially explain smoking’s influence as an aggravating factor for CD. The atmospheric oxidation of group 13 metal alkyls is usually very rapid and uncontrollable, often resulting in combustion.However, controlled oxidation by limited exposure to oxygen gas results in the production of organoperoxide compounds, or alkoxide compounds through the decomposition of the former.It has been well established that the formation of the alkoxide occurs through an intermolecular oxygen transfer, not an intramolecular one.Thus, it is possible to isolate stable complexes bearing a strongly reducing metal-alkyl bond in close proximity of a strongly oxidizing metal-peroxide bond.However, it was demonstrated that spatial requirement plays an important part in the oxidation of group 13 metal alkyls. Recently I became interested in pursuing complexes that bear resemblance to methylalumoxane, a common co-catalyst.
It is involved in myogenesis the insight this reaction brings into the corrosion protection of aluminum
All reactions other than ligand syntheses were performed under an inert atmosphere of argon using either glovebox or Schlenk line techniques. Toluene and hexane were distilled from sodium and phosphorus pentoxide respectively. This mechanism provides insight into how these pyridyl triazole ligands can also act as corrosion inhibitors for aluminum, and further studies are underway to determine their feasibility. The family of cysteine rich proteinscomprises three closely related members, CRP1, CRP2, and CRP3. CRP3 is also known as muscle LIM proteinand has been postulated as a muscle-specific protein. It is involved in the myogenesis and cytoskeletal organization of myocytes. Accordingly, MLP deficiency leads to myocardial hypertrophy followed by cardiomyopathy and heart failure. In myocytes, MLP is localized in the cytoplasm, where it is involved in cytoskeleton modulation. In addition, MLP has been reported to translocate to the nucleus to modulate gene expression during myogenesis and as part of a biomechanical stress response. A Danshensu functional role of MLP in other tissues such as the central nervous system, such as the retina has not yet been described. Amacrine cellsare a heterogeneous group of retinal interneurons and Ganoderic-acid-G synaptically interact with bipolar cells, retinal ganglion cellsand other AC. Mammalian AC have been classified into more than 26 morphologic subtypesthat are distinguishable by specific molecular markers, morphology, size and their neurotransmitters. Cholinergic AC produce the neurotransmitter acetylcholineallowing their specific identification by antibodies against choline acetyltransferase. In rodents, ChAT-immunoreactive AC are detected from embryonic day 17 and produce acetylcholine lifelong. AC are either conventionally located in the inner nuclear layerat the border with the inner plexiform layeror displaced to the ganglion cell layer. The cells of the displaced subpopulation are stimulated by light and therefore termed ONcells. Their dendrites are restricted to the ON sublamina of the IPL, whereas the AC located in the INL are excited in the absence of light. These AC accumulate their dendrites in the OFF-sublamina. As  a consequence of this strict stratification pattern, two distinct ChAT-immunoreactive dendritic layers of cholinergic AC are visible in the IPL. Moreover, cholinergic AC induce spontaneous waves of action potentials in the developing retina, which reportedly facilitates the formation of visual circuits between retinal neurons. This process is apparently driven by the release of acetylcholine. In mammals, the morphology of cholinergic AC proceeds development until the animals open their eyes between postnatal days 13�C15. Concurrently, AC form synapses with direction-selective RGCs during the first two postnatal weeks to establish functional circuits. Islet1, NeuroD or Math3 are reportedly among the few so far identified factors that promote genesis and differentiation of AC, while cell adhesion and guidance molecules such as semaphorins participate in the specific laminar stratification of AC. The current study reports that MLP is expressed in the cytoplasm of cholinergic AC during the late embryonic and the postnatal maturation stage, thereby demonstrating that MLP is also markedly expressed in other tissue than muscle and that MLP is a specific marker for postnatal cholinergic AC with a potential role in AC maturation. MLP is a well-characterized protein, mainly expressed in heart tissue.
a consequence of this strict stratification pattern, two distinct ChAT-immunoreactive dendritic layers of cholinergic AC are visible in the IPL. Moreover, cholinergic AC induce spontaneous waves of action potentials in the developing retina, which reportedly facilitates the formation of visual circuits between retinal neurons. This process is apparently driven by the release of acetylcholine. In mammals, the morphology of cholinergic AC proceeds development until the animals open their eyes between postnatal days 13�C15. Concurrently, AC form synapses with direction-selective RGCs during the first two postnatal weeks to establish functional circuits. Islet1, NeuroD or Math3 are reportedly among the few so far identified factors that promote genesis and differentiation of AC, while cell adhesion and guidance molecules such as semaphorins participate in the specific laminar stratification of AC. The current study reports that MLP is expressed in the cytoplasm of cholinergic AC during the late embryonic and the postnatal maturation stage, thereby demonstrating that MLP is also markedly expressed in other tissue than muscle and that MLP is a specific marker for postnatal cholinergic AC with a potential role in AC maturation. MLP is a well-characterized protein, mainly expressed in heart tissue.