Amongst others in lung cancer. Recent publications evaluated the role of anti-EGFR therapies in biliary tracts carcinomas. Chiorean and colleagues tested Erlotinib and Docetaxel in Advanced and Refractory Hepatocellular and Biliary Cancers in a Phase II Trial of the Hoosier Oncology Group GI06-101. They came to the conclusion that anti-EGFR therapy remains to be an important possibility in these tumors but only with a molecular “targeted” approach. We were able to show that a high EGFR mRNA expression level is associated to patients’ survival and confers a significantly worsened chance to survive longer than one year, 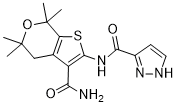 whereas patients with lower EGFR expression had a median survival time of more than 3 years. These results are in agreement with conclusions from other groups that also indicated a higher chance for better outcome in low expression groups. With receiver operating characteristic curve analysis we were able to show that the 35th percentile cut-off of the EGFR mRNA expression could be useful in identifying those patients at risk for shortened survival with a sensitivity of 80% and a specificity of 75%. As Andersen and colleagues recently published the selection of patients from high risk groups may indicate the necessity of AbMole Nitisinone modified treatment and seems to be useful also in cholangiocarcinoma. It has already been discussed by other groups that measuring genes from the angiogenesis pathway seems to be a promising approach in tumors of the biliary tract and pancreas, especially due to their hypoxic nature. In preceding works we were able to shed light on a strong association of Hif1a expression with survival in pancreatic cancer and soft tissue sarcomas. However, this association was not significant in the examined study group of patients with cholangiocarcinoma which is in concordance with discoveries from other groups examining Hif1a in CCC who were also not able to show a correlation of Hif1a expression to survival. VEGFR 2/3 expression was tested in several studies so far. There is however only limited data available for the expression of FLT1/VEGFR1 in cholangiocarcinoma though Rogler and others suggested a potential association with a more aggressive phenotype. We were able to show for the first time that FLT1 seems to be independently associated with overall survival of patients with a biliary tract tumor. Interestingly Kaplan-Meier Analysis revealed that patients with a higher FLT1 expression potentially have a better outcome, though one would anticipate high expression to indicate a more aggressive tumor. Patients with a high expression showed a median overall survival time of 23.6 months and 40% of patients surviving longer than 3 years. The independent association of high FLT1 expression with better outcome was supported by a stepwise multivariate Cox proportional hazards regression model. In this study group FLT1 was the strongest independent factor associated with overall survival. Especially due to the destructive locally invasive behavior and a high rate of distant metastasis we already tested HPSE in pancreatic cancer.
whereas patients with lower EGFR expression had a median survival time of more than 3 years. These results are in agreement with conclusions from other groups that also indicated a higher chance for better outcome in low expression groups. With receiver operating characteristic curve analysis we were able to show that the 35th percentile cut-off of the EGFR mRNA expression could be useful in identifying those patients at risk for shortened survival with a sensitivity of 80% and a specificity of 75%. As Andersen and colleagues recently published the selection of patients from high risk groups may indicate the necessity of AbMole Nitisinone modified treatment and seems to be useful also in cholangiocarcinoma. It has already been discussed by other groups that measuring genes from the angiogenesis pathway seems to be a promising approach in tumors of the biliary tract and pancreas, especially due to their hypoxic nature. In preceding works we were able to shed light on a strong association of Hif1a expression with survival in pancreatic cancer and soft tissue sarcomas. However, this association was not significant in the examined study group of patients with cholangiocarcinoma which is in concordance with discoveries from other groups examining Hif1a in CCC who were also not able to show a correlation of Hif1a expression to survival. VEGFR 2/3 expression was tested in several studies so far. There is however only limited data available for the expression of FLT1/VEGFR1 in cholangiocarcinoma though Rogler and others suggested a potential association with a more aggressive phenotype. We were able to show for the first time that FLT1 seems to be independently associated with overall survival of patients with a biliary tract tumor. Interestingly Kaplan-Meier Analysis revealed that patients with a higher FLT1 expression potentially have a better outcome, though one would anticipate high expression to indicate a more aggressive tumor. Patients with a high expression showed a median overall survival time of 23.6 months and 40% of patients surviving longer than 3 years. The independent association of high FLT1 expression with better outcome was supported by a stepwise multivariate Cox proportional hazards regression model. In this study group FLT1 was the strongest independent factor associated with overall survival. Especially due to the destructive locally invasive behavior and a high rate of distant metastasis we already tested HPSE in pancreatic cancer.
Monthly Archives: March 2019
AQP5 demonstrated to be actively involved at the ovarian bursa seems to be closely related to fluid homeostasis
Substance transport around ovary, thus providing optimal environments for its function. It has long been noticed that just before ovulation, there are dynamic fluid changes within the ovarian bursa, the accumulation and drainage of fluid have been previously implicated to link with the bursa lymphatic system, however, the molecular basis for such rapid fluid transport has not been clarified. In present investigation, we found a transient intra-bursa fluid accumulation and reabsorption within the first 5 hours after PMSG -primed hCG administration. We hypothesized that the rapid fluid regulation within ovarian bursa might be related to the aquaporin family proteins, which are specialized channels for water permeability and showed a wide range of physiological functions. To date, at least nine aquaporin isoforms have been confirmed to be expressed 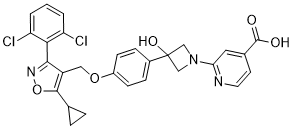 in the male and female reproductive tract. Their specific expression pattern together with their regulation by steroid sex hormones provide indirect evidences of a role for AQPs in reproductive physiology, while the expression of aquaporins in ovarian bursa have not been studied. In this study, we discovered that in adult mouse, pre-ovulation hormonal stimulation induced a rapid fluid accumulation and reabsorption within the ovarian bursa, which is closely associated with the spatial-temporal expressions of two aquaporin proteins AQP2 and AQP5, showing dynamic up and down regulations. At the protein level, AQP2 localized on the peritoneal side while AQP5 on the ovarian epithelial side of ovarian bursa, such interesting Semaphorins are a large family of secreted and membrane bound proteins that act as axonal growth cone guidance molecules arrangements of AQP2 and AQP5 on the distinct compartments suggested their coordinated roles in balancing intra-bursa fluid homeostasis.The ovarian bursa usually contains small amount of fluid except for the substantial increase at the time near ovulation. It has been suggested that the lymphatic stomata within the ovarian bursa might took part in the bursa fluid/substance circulation from the ovarian cavity to the vascular system, mainly due to its closely related structure, and its regulation by steroid hormones. The murine bursa fluid had been described to increase 10 h after hCG administration right before ovulation, and the origin of fluid at this pre-ovulation period was suggested to derive partly from the plasma in the follicle walls and partly from the follicular fluid of ovulating oocytes. Such increased bursa fluid was supposed to lubricate the route by which the ovulated oocytes would pass through later on. In our present study, we found an even earlier and transient intra-bursa fluid accumulation and reabsorption within the first 5 hours after PMSG-primed hCG administration, which seems to be more tightly regulated by hormonal regulation and the coordinated expression of specialized water channel AQP2 and 5. Both AQP2 and AQP5 belong to the classic members of aquaporin family that solely permeable to water. AQP2 is abundantly localized in the principal cells of the kidney, which is critical for the vasopressin-dependent urine concentration.
in the male and female reproductive tract. Their specific expression pattern together with their regulation by steroid sex hormones provide indirect evidences of a role for AQPs in reproductive physiology, while the expression of aquaporins in ovarian bursa have not been studied. In this study, we discovered that in adult mouse, pre-ovulation hormonal stimulation induced a rapid fluid accumulation and reabsorption within the ovarian bursa, which is closely associated with the spatial-temporal expressions of two aquaporin proteins AQP2 and AQP5, showing dynamic up and down regulations. At the protein level, AQP2 localized on the peritoneal side while AQP5 on the ovarian epithelial side of ovarian bursa, such interesting Semaphorins are a large family of secreted and membrane bound proteins that act as axonal growth cone guidance molecules arrangements of AQP2 and AQP5 on the distinct compartments suggested their coordinated roles in balancing intra-bursa fluid homeostasis.The ovarian bursa usually contains small amount of fluid except for the substantial increase at the time near ovulation. It has been suggested that the lymphatic stomata within the ovarian bursa might took part in the bursa fluid/substance circulation from the ovarian cavity to the vascular system, mainly due to its closely related structure, and its regulation by steroid hormones. The murine bursa fluid had been described to increase 10 h after hCG administration right before ovulation, and the origin of fluid at this pre-ovulation period was suggested to derive partly from the plasma in the follicle walls and partly from the follicular fluid of ovulating oocytes. Such increased bursa fluid was supposed to lubricate the route by which the ovulated oocytes would pass through later on. In our present study, we found an even earlier and transient intra-bursa fluid accumulation and reabsorption within the first 5 hours after PMSG-primed hCG administration, which seems to be more tightly regulated by hormonal regulation and the coordinated expression of specialized water channel AQP2 and 5. Both AQP2 and AQP5 belong to the classic members of aquaporin family that solely permeable to water. AQP2 is abundantly localized in the principal cells of the kidney, which is critical for the vasopressin-dependent urine concentration.
FBX8 mediates uniquitination of ADP-ribosylation increased myofibroblast differentiatio
These findings point to aberrant myofibroblast differentiation as an important contributor to airway remodeling in late-stage CF, and suggest the myofibroblast as a novel mediator of CF pulmonary destruction. The results also provide important insight regarding the process of tissue scarring and remodeling that contributes to CF respiratory decline. Myofibroblast differentiation occurs normally in the setting of tissue injury, TGF-b stimulation, and mechanical strain. The myofibroblast contributes to healing by approximating wound edges and promoting AbMole Folic acid extracellular matrix formation. In health, myofibroblasts undergo apoptosis following resolution of tissue injury. In diseases such as IPF, aberrant myofibroblast persistence results in tissue fibrosis and parenchymal contracture. Recently, Ulrich et al noted increased myofibroblasts and ceramide deposition in peripheral CF alveolar tissue. Ziobro et al subsequently demonstrated a palliative effect of blunting ceramide accumulation in the CF murine model.Therefore, it is of great interest to search for valuable factors for prognosis prediction and novel therapeutic strategies. The ubiquitin-dependent proteolytic pathway is an important mechanism of protein abundance regulation in eukaryotes. F-box proteins are critical components of the SCF uniquitin-protein ligase complex and are involved in the ubiquitin-dependent proteolytic pathway. So far, more than 70 putative F-box proteins have been AbMole Lesinurad identidied in human genome, although the function and their substrates of most F-box proteins remain elusive. Only several members of F-box proteins such as Skp2 and Fbw7 have been well-studied in cancer. Recent studies revealed that Skp2 and Fbw7 were closely associated with tumor progression and metastasis. FBX8 is a novel component of F-box proteins, which contains an F-box domain and a putative Sec7 domain. FBX8 was originally identified as a Skp1-binding protein. It has E3 ligase activity mediating the ubiquitination of the GTP-binding protein ARF6. Moreover, FBX8 over-expression could inhibit ARF6-mediated cell invasion activity in breast cancer cells. FBX8 was found to be a novel c-Myc binding protein and cMyc induced cell invasive activity through the inhibition of FBX8 effects on ARF6 function. Expression of FBX8 has been reported to be lost in some tumor cells, such as breast cancer and lung cancer cells. Till now, the molecular and biological functions of FBX8 in the development and progression of HCC remain unknown. To address this question, we evaluated FBX8 expression in HCC cell lines and clinical tissues, investigated the effect of FBX8 on the proliferation, invasion and metastasis of HCC cells. FBX8 is a novel member of the F-box protein family which is characterized by an approximately 40 amino acid motif, the Fbox. The F-box proteins constitute one of the four subunits of the ubiquitin protein ligase complex called SKP1-cullin-F-box, which is involved in phosphorylation-dependent ubiquitination. Till now, only three recent papers have discussed the function of FBX8 in cancer.
m1R9 methyltransferase subcomplex and the molecular mechanism of SDR5C1-mediated Ab toxicity remains unclear
SDR5C1 is proposed to be a crucial player in Abinduced mitochondrial dysfunction and, as a result, in AD. However, the biological significance of the Ab-SDR5C1 interaction and how it links to mitochondrial dysfunction is largely unclear. Moreover, while SDR5C1 appears to be vital for mitochondrial function, this does not appear to be due to its dehydrogenase function; mitochondrial abnormalities associated with mutations in HSD17B10 do not seem to correlate with the residual dehydrogenase activity, AbMole 4-(Aminomethyl)benzoic acid suggesting that another function of SDR5C1 could actually be compromised and responsible for the mutation-associated neurodegenerative disease. The discovery of SDR5C1’s essential role in tRNA maturation suggested a possible dehydrogenase-independent pathway leading from the interaction of Ab with SDR5C1 to mitochondrial dysfunction. Specifically, we hypothesized that the binding of Ab could impair the SDR5C1-dependent tRNA:m1R9 methyltransferase or mtRNase P activity. In conclusion, the proposed deleterious effect of Ab on mitochondrial function cannot be explained by an inhibition of human mtRNase P or its tRNA. In considering the role of inflammation in prostate cancer, one of the confounding observations is that chronic immune inflammation appears to play a crucial role in both Prostate Cancer and Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia. BPH is clearly a late-onset phenomenon, and results from the PCPT trial strongly suggest that a diagnosis of BPH is not associated with elevated prostate cancer risk, however, a recent report suggests that hospitalization and surgery for BPH can increase the risk of prostate cancer specific death by as much as 8 fold. Here, the wounding associated with surgery is consistent with the hypothesis that a wound response is associated with the genesis of aggressive prostate cancers. This contrasts with the tumor-associated macrophages present in the tumor microenvironment. In general these macrophages are thought to gradually switch from an M1 to an M2 phenotype during tumor progression, leaving an M2-like phenotype that still produces reactive nitrogen and reactive oxygen species. For these reasons, stromal cells in the tumor-associated microenvironment are expected to experience exposure to both ROS and RNS. Thioredoxin, a small redox protein, could be involved in the stromal response to this exposure. Thioredoxin expression appears to be a link between oxidative stress and inflammation in that it is a chemoattractant for neutrophils, monocytes and T-cells. Thioredoxin interacting protein partners, like TXNRD2 which reduces H2O2 to H2O, and TXNRD1 which appears to be rate limiting in the removal of Snitrosylated cysteine residues from caspase-3 and perhaps other S-nitrosylated proteins.Further, heregulin binding to ErbB3 results in the dissociation of EBP1, which binds to nuclear AKT and suppresses caspase-activated DNase to prevent DNA fragmentation. Our preliminary data suggest EBP1 and ErbB3 colocalize in the somatic cells of perinatal hamster ovaries and heregulin exposure of P6 ovarian cells in culture results in ERK1 phosphorylation.
The low-grade or chronic inflammation in NAFLD and insulin resistance resulting from lipid accumulation in liver
The liver is an important principal organ in the maintenance 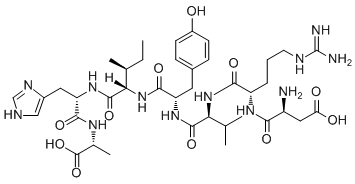 of glucose homeostasis and energy storage for the conversion of excess dietary nutrients into triglycerides. Under HFD feeding conditions, excess TG in the liver induces fatty liver and eventually insulin resistance. HFD feeding increased the body weight gradually along the time course, 2 weeks after HFD. HFD rats body weight was significantly higher edna techniques efficient inventory monitoring programs sensitive species compared to NCD rats, and FX treatment tended to decrease the body weight although not significantly. The weight of various tissues, including SCF, EF, and pancreas, was similar amongst all groups. The liver weight and relative liver weight in FX treated rats were significantly lower than that of HFD rats, suggesting that FX has a beneficial effect on lowering TG content in the liver. It has been shown that FX has hepatotoxicity at a high dosage, while the doses we used here didn’t induce a further alteration of serum ALT and AST level compared to rats on HFD alone. When administrated to normal chow diet rats, FX even tended to decrease the ALT levels, implying a potential liver protective effect. TG is thought to be a surrogate marker of disrupted insulin signal. In other words, hepatic insulin resistance is associated with the accumulation of TG and FA metabolites. The rate of glucose disposal and insulin sensitivity were measured by OGTT and IPITT. FX treated rats had significantly lower levels of blood glucose after administration of an exogenous load of glucose, suggesting an enhanced glucose disposal. When challenged with excessive amounts of insulin, FX treatment showed drastically reduced level of blood glucose and improved glucose disposal in HFD rats, suggesting that FX increased insulin sensitivity. The raised insulin sensitivity could also reflect less lipid accumulation in the liver indirectly. FX treatment significantly decreased liver TG content. Morphologically, the liver of HFD rats showed abundant and large lipid droplets, and obvious increase of liver derangement compared to that of NCD rats. However, the liver of FX rats had fewer lipid droplets and more normal liver morphology, suggesting a beneficial effect of FX on preventing lipid accumulation and reversal of disrupted structure of the liver. In addition, FX may also exert liver protective effect via inhibition of HFDinduced inflammation, since our results showed that FX decreased gene expression of inflammatory cytokines. To explore the possible mechanisms of FX on decreasing liver lipids accumulation, we investigated the expression levels of several genes related to fatty acid transport, and lipid metabolism including lipogenesis and b-oxidation. ChREBP regulates the balance between glycogen and triglyceride storage by coordinately regulating glycolytic and lipogenic gene expression. The results showed that the level of ChREBP was significantly higher in the liver of rats fed HFD compared with that of NCD. FX effectively inhibited the raise of ChREBP expression. Expression of ChREBP transcriptional targets FAS and ACC1 also strongly correlates with ChREBP expression. FAS catalyze the last step in fatty acid biosynthesis, and thus, it is believed to be a major determinant of the maximal hepatic capacity to generate fatty acids by de novo lipogenesis. FX markedly decreased the HFD-induced high expression of ACC1 and FAS. The trend of SCD1 influenced by FX was similar to that of FAS but only at high dose. There is evidence suggested that transgenic hepatic over-expression of SREBP-1c produced a fatty liver and a 4-fold increase in the rate of hepatic fatty acid synthesis with increase in lipogenic genes like FAS, ACC, and SCD. Here, we showed that hepatic SREBP1c mRNA in HFD rats was increased. FX treatment generated a significant decreasing effect on its expression paralleled with the change in ChREBP expression.
of glucose homeostasis and energy storage for the conversion of excess dietary nutrients into triglycerides. Under HFD feeding conditions, excess TG in the liver induces fatty liver and eventually insulin resistance. HFD feeding increased the body weight gradually along the time course, 2 weeks after HFD. HFD rats body weight was significantly higher edna techniques efficient inventory monitoring programs sensitive species compared to NCD rats, and FX treatment tended to decrease the body weight although not significantly. The weight of various tissues, including SCF, EF, and pancreas, was similar amongst all groups. The liver weight and relative liver weight in FX treated rats were significantly lower than that of HFD rats, suggesting that FX has a beneficial effect on lowering TG content in the liver. It has been shown that FX has hepatotoxicity at a high dosage, while the doses we used here didn’t induce a further alteration of serum ALT and AST level compared to rats on HFD alone. When administrated to normal chow diet rats, FX even tended to decrease the ALT levels, implying a potential liver protective effect. TG is thought to be a surrogate marker of disrupted insulin signal. In other words, hepatic insulin resistance is associated with the accumulation of TG and FA metabolites. The rate of glucose disposal and insulin sensitivity were measured by OGTT and IPITT. FX treated rats had significantly lower levels of blood glucose after administration of an exogenous load of glucose, suggesting an enhanced glucose disposal. When challenged with excessive amounts of insulin, FX treatment showed drastically reduced level of blood glucose and improved glucose disposal in HFD rats, suggesting that FX increased insulin sensitivity. The raised insulin sensitivity could also reflect less lipid accumulation in the liver indirectly. FX treatment significantly decreased liver TG content. Morphologically, the liver of HFD rats showed abundant and large lipid droplets, and obvious increase of liver derangement compared to that of NCD rats. However, the liver of FX rats had fewer lipid droplets and more normal liver morphology, suggesting a beneficial effect of FX on preventing lipid accumulation and reversal of disrupted structure of the liver. In addition, FX may also exert liver protective effect via inhibition of HFDinduced inflammation, since our results showed that FX decreased gene expression of inflammatory cytokines. To explore the possible mechanisms of FX on decreasing liver lipids accumulation, we investigated the expression levels of several genes related to fatty acid transport, and lipid metabolism including lipogenesis and b-oxidation. ChREBP regulates the balance between glycogen and triglyceride storage by coordinately regulating glycolytic and lipogenic gene expression. The results showed that the level of ChREBP was significantly higher in the liver of rats fed HFD compared with that of NCD. FX effectively inhibited the raise of ChREBP expression. Expression of ChREBP transcriptional targets FAS and ACC1 also strongly correlates with ChREBP expression. FAS catalyze the last step in fatty acid biosynthesis, and thus, it is believed to be a major determinant of the maximal hepatic capacity to generate fatty acids by de novo lipogenesis. FX markedly decreased the HFD-induced high expression of ACC1 and FAS. The trend of SCD1 influenced by FX was similar to that of FAS but only at high dose. There is evidence suggested that transgenic hepatic over-expression of SREBP-1c produced a fatty liver and a 4-fold increase in the rate of hepatic fatty acid synthesis with increase in lipogenic genes like FAS, ACC, and SCD. Here, we showed that hepatic SREBP1c mRNA in HFD rats was increased. FX treatment generated a significant decreasing effect on its expression paralleled with the change in ChREBP expression.